As the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector navigates its digital transformation journey, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data governance emerge as pivotal components. Adopting AI technologies and implementing robust data governance policies can drive innovation and ensure compliance in the financial industry. This blog discusses the transformative potential of AI in BFSI and underscores the importance of data governance in realizing these benefits.
Evolving into an AI-First Bank
AI has the potential to revolutionize banking by enhancing customer experiences, improving operational efficiency, and uncovering new opportunities. According to McKinsey, AI could add up to $1 trillion in value annually to global banking. Banks that successfully integrate AI into their operations are well-positioned to lead in this evolving landscape.
Let us look at a few key areas in a diagram where AI can improve the customer experience while simplifying backend processes.
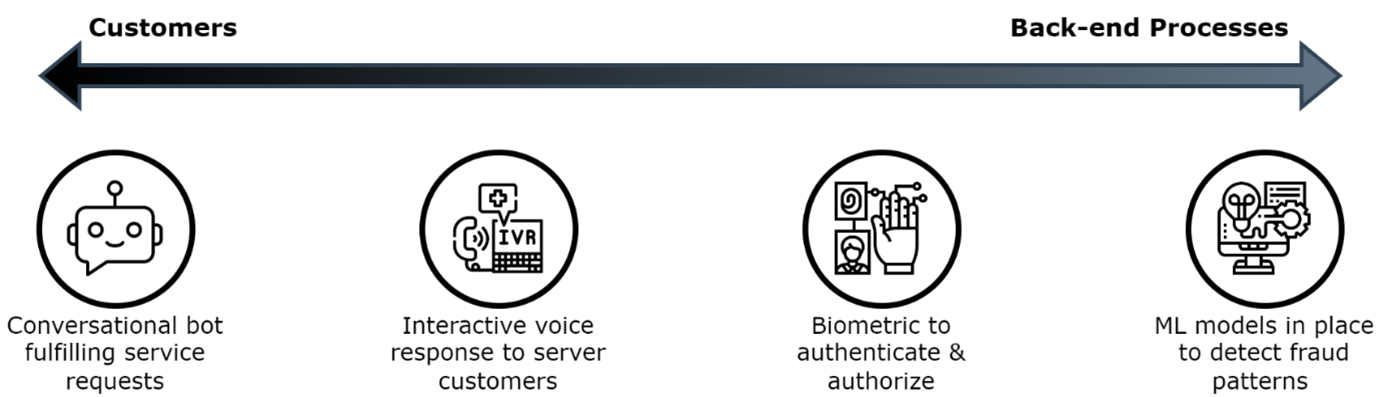
Key Areas Where AI Can Make an Impact
Personalized Services
AI customizes product recommendations and services for each customer, enhancing satisfaction and fostering loyalty. Through extensive data analysis, it gains insights into customer behaviors, preferences, and needs. This enables banks to offer personalized financial advice, customized product offerings, and proactive customer service, resulting in enhanced customer experiences. For example, AI-driven chatbots provide instant customer support, addressing queries and offering personalized financial advice based on individual spending patterns and financial goals.
Operational Efficiency
Automation reduces errors and optimizes resource utilization. AI-driven automation streamlines back-office operations, reduces manual intervention, and minimizes human error. This leads to faster processing times, cost savings, and improved accuracy in tasks such as data entry, document verification, and transaction processing.
Example: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can handle routine tasks such as account opening, loan processing, and compliance reporting, freeing up human employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Risk Management
AI enhances fraud detection, credit risk assessment, and compliance monitoring. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics, AI can identify unusual patterns and behaviors indicative of fraudulent activity. Additionally, AI can assess credit risk more accurately by analyzing a wider range of data points, including non-traditional data sources.
Example: AI-powered systems can monitor transactions in real-time, flagging suspicious activities and preventing potential fraud before it occurs. In credit risk assessment, AI models can evaluate the creditworthiness of borrowers more precisely, leading to better-informed lending decisions.
Importance of Data Governance in BFSI Institutions
The BFSI (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) sector manages extensive amounts of sensitive data, necessitating strong data governance frameworks. Robust data governance is vital for ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, protecting data security, and maintaining high data quality. These elements are crucial for upholding trust, ensuring operational integrity, and enhancing the overall efficiency of BFSI institutions.
Core Principles of Data Governance
1. Comprehensive Data Quality Management (DQM)
- Continuous Assessment: Regular monitoring and assessment of data quality to identify and rectify inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and incompleteness.
- Improvement Processes: Implementation of strategies and tools for continuous data quality improvement, ensuring data remains reliable and accurate over time.
- Data Standards: Establishing and enforcing data standards and guidelines to maintain consistency and reliability across all data sources.
2. Stringent Security Measures
- Data Protection: Implementing advanced security measures such as encryption, access controls, and multi-factor authentication to safeguard data against breaches and unauthorized access.
- Incident Response: Developing and maintaining an effective incident response plan to quickly address and mitigate any security breaches or vulnerabilities.
- Risk Management: Continuously assessing and managing risks associated with data security to preemptively address potential threats.
3. Regulatory Compliance
- Adherence to Regulations: Ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), which govern data privacy and protection.
- Audit Trails: Maintaining detailed audit trails and documentation to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and to facilitate regulatory audits.
- Regular Audits: Conducting regular internal and external audits to ensure ongoing compliance with relevant regulations and standards.
4. Efficient Data Access
- Role-Based Access: Implementing role-based access controls to ensure that data is accessible only to authorized users based on their roles and responsibilities.
- Data Availability: Ensuring data is readily available to authorized users when needed, supporting timely decision-making and operational efficiency.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Developing intuitive and user-friendly data access interfaces to facilitate easy and efficient data retrieval.
5. Data Lifecycle Management
- Data Creation and Acquisition: Implementing standardized processes for data creation and acquisition to ensure data integrity from the outset.
- Data Maintenance: Regularly updating and maintaining data to ensure its accuracy and relevance.
- Data Disposal: Establishing secure data disposal practices to safely and effectively remove data that is no longer needed, ensuring compliance with data retention policies and regulations.
6. User Education and Accountability
- Training Programs: Conducting regular training programs to educate users about data governance policies, procedures, and their responsibilities.
- Policy Awareness: Ensuring all users are aware of and understand the data governance policies and the importance of adhering to them.
- Accountability Mechanisms: Implementing mechanisms to hold users accountable for their data-related actions, encouraging responsible data handling and usage.
Conclusion
By embracing AI and implementing robust data governance frameworks, BFSI institutions can unlock new growth opportunities and enhance customer experiences. AI-driven analytics can provide deeper insights, improve decision-making, and drive innovation. Effective data governance ensures these AI initiatives are built on a foundation of high-quality, secure, and compliant data.
A successful legacy modernization involves developing a scalable, reliable, and maintainable enterprise data strategy. This strategy not only supports current operational needs but also prepares the institution for future growth and regulatory changes. By staying relevant and increasing growth through these means, BFSI institutions can maintain their competitive edge in an evolving financial landscape.
Ultimately, robust data governance combined with advanced AI capabilities positions BFSI institutions to thrive in the digital age, ensuring they remain compliant, secure, and customer-focused.

