As pioneers in creating tech breakthroughs, Experion aligns with the future of smart energy and mobility, where innovation meets sustainability.
The rise of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology is transforming Electric vehicles (EVs) into power players in the energy world. EVs represent a significant shift in the automotive industry, relying on clean, renewable energy sources instead of traditional fossil fuels. The cornerstone of EV functionality lies in their ability to recharge using electricity drawn from the grid or other energy sources. Charging an EV involves transferring electrical energy to its battery pack through dedicated EV chargers, which can range from basic Level 1 chargers to advanced DC fast chargers.
As the global focus intensifies on sustainability, EV charging technology continues to evolve, integrating smart features such as dynamic load management, real-time energy monitoring, and renewable energy compatibility. This evolution not only facilitates faster and more efficient charging but also contributes to reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
Importance of Bidirectional Charging in Modern EV Ecosystems
Electric Vehicle bidirectional charging technology has emerged as a transformative force in modern EV ecosystems. By enabling two-way energy transfer, EVs transcend their traditional role as consumers of energy to become dynamic assets in the energy ecosystem. This capability is especially significant in addressing contemporary energy challenges:
- Grid Stability: By feeding energy back to the grid, EVs can help stabilize voltage and frequency levels during periods of high demand or fluctuations in renewable energy generation.
- Reduced Fossil Fuel Dependency: By promoting renewable energy integration, bidirectional charging reduces reliance on fossil fuels, accelerating the transition to cleaner energy sources.
- Financial Opportunities for EV Owners: Bidirectional charging opens avenues for EV owners to monetize excess energy by participating in energy markets, offering services like peak shaving, or providing emergency backup power to homes and businesses.
- Emergency Preparedness: EVs equipped with bidirectional capabilities can act as mobile power supplies during outages, contributing to energy resilience.
What is Bidirectional EV Charging?

Bidirectional EV charging, also known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, represents an advanced approach to EV charging. Unlike conventional systems, which solely transfer energy from the grid to the vehicle, bidirectional systems allow energy to flow in both directions. This means that an EV can charge its battery from the grid and also discharge stored energy back into the grid or other connected systems.
This technology effectively transforms EVs into mobile energy storage units, capable of contributing to energy distribution, reducing peak loads, and serving as backup power sources. The versatility of bidirectional charging positions it as a key enabler in the transition to a more decentralized and resilient energy infrastructure.
How Bidirectional Charging Differs from Conventional Charging
The primary distinction between conventional and bidirectional charging lies in the direction of energy flow:
- Conventional Charging: Energy flows unidirectionally, from the grid to the EV. This method is straightforward, designed only to replenish the vehicle’s battery.
- Bidirectional Charging: Energy flows bidirectionally, enabling the EV to function as an energy resource. This two-way interaction allows EVs to discharge energy into the grid, home, or building, making them active participants in energy management.
The advanced capabilities of bidirectional charging introduce new functionalities, such as supporting renewable energy integration and enabling energy trading, which are absent in conventional systems.
Types of Bidirectional Charging
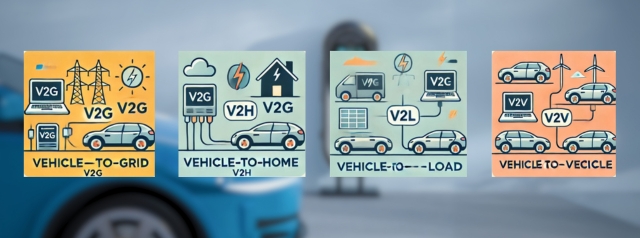
Overview of Different Types
Bidirectional charging encompasses several configurations, each tailored to specific use cases:
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G):
- Facilitates the transfer of energy from EVs to the grid.
- Used for grid stabilization, frequency regulation, and peak load management.
- Supports renewable energy integration by balancing supply and demand.
Vehicle-to-Home (V2H):
- Allows EVs to supply power directly to household appliances and systems.
- Supplies backup power during blackouts or periods of elevated grid prices.
- Supports energy independence and cost savings for homeowners.
Vehicle-to-Building (V2B):
- Extends V2H capabilities to larger commercial and industrial facilities.
- Helps reduce electricity costs by leveraging stored EV energy during peak demand periods.
- Enhances energy resilience in critical operations.
Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V):
- Facilitates energy transfer between two EVs.
- Useful in scenarios such as emergency charging or peer-to-peer energy sharing.
- Promotes collaboration and community energy solutions.
Key Features and Applications
Key Features
- Enhanced Grid Stability: EVs contribute to balancing grid loads, ensuring consistent voltage and frequency levels.
- Peak Load Shaving: By discharging stored energy during peak demand, bidirectional charging reduces strain on the grid.
- Frequency Regulation: Precise energy contributions help maintain grid frequency within acceptable limits.
- Renewable Energy Integration: EVs can store surplus renewable energy and discharge it when needed, minimizing wastage.
- Emergency Power Supply: EVs serve as reliable backup power sources during outages, ensuring critical systems remain operational.
- Revenue Generation: EV owners can earn income by selling stored energy or providing grid services.
Applications
1. Residential Applications (V2H):
- Backup power during outages.
- Cost optimization by discharging stored energy during peak electricity rates.
2. Commercial and Industrial Applications (V2B):
- Reducing operational costs by using EVs as a supplemental power source.
- Enhancing energy efficiency in large facilities.
3. Grid Services (V2G):
- Supporting renewable energy integration.
- Stabilizing grid operations through frequency regulation and voltage control.
4. Disaster Relief:
- Providing essential power during emergencies or natural disasters.
- Facilitating rapid deployment of mobile energy solutions.
5. Electric Vehicle Fleets:
- Fleet vehicles equipped with bidirectional charging can collectively serve as a significant energy resource.
- Ideal for industries like public transportation, logistics, and shared mobility.
V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid) Charging: Power Back to the Grid
How V2G Works
Imagine your electric vehicle not just as a car but as a contributor to the larger energy ecosystem. That’s the magic of V2G technology. It’s powered by custom bidirectional EV charging software, enabling a two-way energy dance between your EV and the grid.
Here’s how it works:
- During Peak Hours: Your EV becomes a team player, sharing a portion of its stored energy to lighten the grid’s load when demand soars—like during those summer evenings when every AC is running full blast.
- During Off-Peak Hours: Your EV quietly recharges itself when electricity is cheaper, ensuring you’re ready for the road and the next energy-sharing opportunity.
V2G charging turns your car into more than just a ride; it’s a partner in creating a stable, efficient energy network.
Benefits for Energy Management and Grid Stability
So why should your car double as an energy expert? Here are a few reasons that might get you excited:
- Peak Load Shaving: Think of your EV swooping in like a superhero to save the grid from overloading. By sharing energy during high-demand hours, it reduces the need for costly and environmentally taxing “peaker plants.”
- Frequency Regulation: Ever seen how a conductor ensures an orchestra stays in tune? Your EV does something similar for the grid, helping it stay balanced and reliable.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Picture a sunny afternoon when solar panels generate more power than we can use. Your EV steps in as a storage vault, holding that clean energy until it’s needed later.
- Grid Resilience: In emergencies or outages, your EV can keep the lights on—not just in your home but potentially in hospitals or shelters too. It’s a rolling lifeline.
Real-World Use Cases and Examples
The concept of V2G is already stepping out of the lab and into real life:
Utility Programs
Forward-thinking energy providers reward EV owners for sharing their battery power during peak demand. Programs like those in California allow owners to earn extra cash or lower their energy bills, making charging an income-generating activity while stabilizing the grid.
Fleet Operators
Companies managing EV fleets, like delivery vans and buses, use V2G to cut energy costs and stabilize the grid. By charging during off-peak hours and discharging surplus energy during peak times, they maximize efficiency and support sustainability efforts.
Residential Applications
Some EV owners are turning their vehicles into grid-support tools, earning incentives while contributing to cleaner energy. With V2G, cars not only charge but also supply power to their homes or neighborhoods during high-demand periods.
V2H (Vehicle-to-Home) Charging: Powering Homes with EVs
Functionality and Integration with Home Energy Systems
Now imagine this: your EV isn’t just powering your journeys; it’s powering your home too. That’s the beauty of V2H charging, where your car becomes your personal backup generator.
Here’s how it works:
- During grid outages, your EV steps in to keep essential appliances like lights, refrigerators, or even medical devices running smoothly.
- It syncs seamlessly with home energy management systems (HEMS), optimizing energy flow between your car, home, and even rooftop solar panels.
With vehicle-to-home technology, your EV becomes the quiet hero that keeps your life moving, even when the power goes out.
Backup Power and Energy Cost Savings
V2H isn’t just about emergencies; it’s a game-changer for everyday life too:
- Backup Power: Whether it’s a storm cutting off electricity or a routine outage, your EV ensures the essentials are always powered. No more fumbling for candles!
- Energy Cost Savings: Charge your EV during off-peak hours, when electricity is cheapest, and use that stored power during peak hours to lower your energy bills. Add rooftop solar to the mix, and you’re practically living off the grid.
Implementation Scenarios
Wondering how V2H could fit into your life? Here are some ideas:
- New Home Construction: Building a new home? Integrating V2H systems during construction makes everything seamless and future-proof.
- Retrofitting Existing Homes: Even older homes can join the V2H revolution with a few upgrades to the electrical system and a bidirectional charger.
- Community-Level V2H: Imagine an entire neighborhood of connected V2H systems forming a virtual power plant, supporting not just homes but the local grid as well.
With bidirectional EV charging leading the way, your EV is no longer just a mode of transport, it’s a partner in reshaping how we consume and share energy. From V2G charging stabilizing the grid to V2H charging powering homes, the possibilities are as exciting as they are transformative. What’s next? Maybe your EV will even power your neighbor’s home through V2L charging.
V2L (Vehicle-to-Load) Charging: Power on the Go
V2L, or Vehicle-to-Load charging, redefines the functionality of electric vehicles by transforming them into mobile power stations. It allows the energy stored in an EV’s battery to power external devices and appliances, making it a practical solution for situations requiring portable electricity. With the use of a special adapter connected to the EV’s charging port, V2L provides standard outlets that can support various electrical loads. Whether it’s for leisure, emergencies, or work, V2L adds an entirely new dimension to what EVs can do.
For outdoor enthusiasts, V2L is a game-changer. It enables the use of camping equipment like portable refrigerators, lights, and cooking appliances, turning any outdoor adventure into a comfortable and connected experience. In emergencies, such as power outages, V2L becomes a lifeline, supplying power to essential home appliances like lights, fans, and medical devices. Additionally, it finds utility in construction and DIY projects, where tools and equipment can be powered directly from the EV, eliminating the need for separate generators.
Several modern EVs already support V2L capabilities, including the Hyundai IONIQ 5, Kia EV6, and Ford F-150 Lightning. As more automakers recognize the growing demand for versatile energy solutions, V2L is quickly becoming a standard feature in new electric vehicles, pushing the boundaries of what EVs can offer beyond mobility.
V2V (Vehicle-to-Vehicle) Charging: EVs Sharing Power
V2V charging, or Vehicle-to-Vehicle charging, introduces an innovative approach to energy sharing, enabling direct power transfer between two EVs. This capability relies on specialized charging cables and communication protocols to ensure efficient and safe electricity exchange. By leveraging the bidirectional flow of power, V2V opens up possibilities for emergency assistance and collaborative energy use among EV owners.
One of the most practical applications of V2V charging is providing emergency assistance. When an EV is stranded with a depleted battery, V2V allows a nearby vehicle to transfer enough charge to get it moving again, ensuring drivers can reach a charging station or continue their journey. Beyond emergencies, V2V has the potential to support the energy grid by enabling EVs to share power during peak demand or outages, creating a decentralized and resilient energy network. Looking further ahead, V2V could facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading, empowering EV owners to buy or sell electricity directly from one another, fostering a collaborative energy ecosystem.
Although still in its infancy, V2V technology promises a revolutionary shift in how we perceive energy sharing and management. As EV adoption grows and supporting infrastructure develops, the integration of V2V into daily life could unlock a more flexible and community-driven approach to energy consumption. These advancements, alongside innovations like V2L, are transforming electric vehicles into versatile platforms that extend far beyond transportation, highlighting their role as dynamic assets in a future shaped by sustainable energy solutions.
Much like V2G chargers powering grids, our solutions at Experion power businesses with forward-thinking technologies tailored for impact.
Benefits of Bidirectional EV Charging
Enhanced Grid Stability
Bidirectional EV charging plays a pivotal role in strengthening grid reliability, allowing electric vehicles to contribute actively to energy management:
- Peak Load Shaving: During high-demand periods, EVs discharge power back to the grid, easing strain and reducing the risk of blackouts. This not only helps utilities but also ensures a consistent power supply for consumers.
- Frequency Regulation: V2G technology is highly responsive to fluctuations in grid frequency, acting as a stabilizing force to maintain reliable energy flow.
- Renewable Energy Integration: EVs store excess energy generated during sunny or windy days, releasing it back when demand spikes or renewable generation dips, creating a smoother, more balanced energy system.
Improved Energy Efficiency
EV Bidirectional charging offers smarter ways to manage energy use, reducing costs and optimizing renewable energy consumption:
- Time-of-Use Charging: EVs charge when electricity is cheapest, typically during off-peak hours, lowering energy bills while aligning with grid demand cycles.
- Solar Integration: Excess solar energy from rooftop panels can be stored in EVs and used later, minimizing grid reliance and supporting greener energy consumption.
Increased Grid Resilience
When unexpected outages or emergencies strike, bidirectional charging transforms EVs into mobile power stations:
- Emergency Power Supply: EVs can power homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure, ensuring essential devices and appliances stay operational during grid failures.
Revenue Generation for EV Owners
By participating in grid-support activities, EV owners can turn their vehicles into income-generating assets:
- Grid Services: Programs like frequency regulation and peak load shaving allow owners to earn while contributing to energy stability.
Reduced Carbon Emissions
Bidirectional charging directly supports a cleaner energy future:
- By storing and redistributing renewable energy, EVs decrease reliance on fossil fuels and help decarbonize the energy sector.
- This results in tangible environmental benefits, including lower greenhouse gas emissions and better air quality.
Challenges and Limitations of Bidirectional EV Charging
Technical Challenges
Infrastructure
The transition to bidirectional charging demands significant upgrades:
- Existing grid systems require modernization to handle two-way energy flows effectively.
- Widespread deployment of V2G-capable charging stations necessitates substantial investment and planning.
Compatibility
Ensuring seamless integration across various technologies is another hurdle:
- EVs, charging stations, and grid systems must align, which can be challenging given the diversity in models and platforms.
- Standardized communication protocols and universal charging standards are essential for scalability.
Policy and Regulatory Barriers
Government policies and market frameworks need to evolve:
- Clear incentives and regulations are vital to encourage V2G adoption and address concerns like grid security and data privacy.
- Mechanisms for compensating EV owners fairly for their contributions to grid services must be established to ensure economic viability.
Cost Considerations for Users
Adoption costs and concerns about long-term implications may deter some consumers:
- The upfront cost of bidirectional chargers can be prohibitive for individuals or small businesses.
- Potential impacts on EV battery lifespan raise concerns about maintenance and replacement costs.
- Compensation models must reflect the value EV owners provide to the grid to foster widespread participation.
Future Prospects of Bidirectional EV Charging
Innovations and Market Trends
Bidirectional EV charging is on the cusp of transformative advancements:
- Breakthroughs in battery technology, power electronics, and communication systems will enhance efficiency, reliability, and affordability.
- The growing adoption of renewable energy, coupled with decreasing EV costs, will propel the market for bidirectional charging solutions.
Potential Impact on Renewable Energy Integration
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, bidirectional charging will be indispensable:
- EVs can act as distributed energy storage units, storing surplus solar and wind power and redistributing it during demand peaks or production lulls.
- This integration helps address the inherent variability of renewable energy sources, creating a more dependable and sustainable grid.
Long-term Benefits for Consumers and the Environment
The long-term advantages of bidirectional charging extend far beyond convenience:
- Consumers can actively participate in energy management, reducing dependence on traditional utilities and lowering their electricity costs.
- On a larger scale, bidirectional charging will accelerate the transition to cleaner energy systems, delivering environmental benefits such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions and healthier air quality.
Bidirectional EV charging is not just a technological evolution; it’s a pivotal step towards a future where vehicles play an integral role in creating sustainable, resilient, and efficient energy ecosystems.
How Experion Can Offer Support
 At Experion, we recognize the transformative potential of bidirectional EV charging in reshaping the energy and transportation landscape. Our expertise in custom software development and innovative solutions for transport and logistics uniquely positions us to drive advancements in this emerging field.
At Experion, we recognize the transformative potential of bidirectional EV charging in reshaping the energy and transportation landscape. Our expertise in custom software development and innovative solutions for transport and logistics uniquely positions us to drive advancements in this emerging field.
- Custom Bidirectional EV Charging Software: We specialize in developing intelligent software tailored to enhance V2G, V2H, V2L, and V2V charging technologies. From enabling seamless communication between EVs and the grid to optimizing energy flow, our solutions ensure reliable, efficient, and user-friendly operations.
- Integration with Renewable Energy Systems: By leveraging our experience in smart energy solutions, we help integrate bidirectional charging systems with renewable energy sources like solar and wind, enabling efficient energy utilization and reduced dependency on fossil fuels.
- Scalable Platforms for EV Ecosystems: Experion’s platforms are designed to support the evolving needs of EV owners, fleet operators, and utilities. Whether it’s real-time energy management or peer-to-peer energy trading, our scalable systems provide a seamless user experience while ensuring compliance with global standards.
- Partnerships with Industry Leaders: Our collaborations with leading automotive and energy companies allow us to create interoperable, future-ready solutions that address the challenges of infrastructure, compatibility, and regulation.
By combining our product engineering expertise with insights into the unique demands of the EV ecosystem, Experion is helping shape a sustainable and innovative future for mobility and energy management.
Conclusion
Bidirectional EV charging is more than a technological leap; it’s a vision for a cleaner, smarter, and more sustainable future. By enabling electric vehicles to interact dynamically with the grid, homes, and other vehicles, this technology transforms EVs into active contributors to energy management. From enhancing grid stability and integrating renewable energy to offering backup power and new revenue opportunities, the potential benefits are vast and far-reaching.
While challenges like infrastructure upgrades, standardization, and policy development remain, the rapid pace of innovation and growing global commitment to sustainability signal a promising future. As this ecosystem matures, bidirectional charging will redefine the relationship between energy and mobility, empowering individuals, businesses, and communities to contribute to a more resilient and eco-friendly world.
Key Takeaways
- Bidirectional charging turns EVs into mobile energy assets.
- V2G helps stabilize the grid during peak demand.
- V2H powers homes during outages and reduces energy costs.
- V2L allows EVs to run devices and tools anywhere.
- V2V enables EVs to share power with each other.
- EVs support renewable energy by storing and redistributing excess power.
- EV owners can earn revenue through grid services.
- Infrastructure upgrades are crucial for widespread adoption.
- Standardization of charging systems ensures compatibility.
- Policy incentives will drive adoption and growth.
The road ahead is electric, and with bidirectional charging at its core, we’re not just moving forward; we’re driving toward a future powered by collaboration, innovation, and sustainability. With every solution we craft, Experion reaffirms its commitment to making technology that not only works but transforms industries.

