Usability testing is a method for evaluating a product by testing it with actual users who will use the product. This is achieved by observing the users’ behavior as they interact with your product. Through this process, we can identify areas where they struggle, experience frustrations, or encounter difficulties in completing specific tasks.
Usability testing holds significant importance because it allows designers and developers to uncover numerous design issues and gain insights into user behavior and preferences while using the product. Additionally, it helps identify opportunities for improving the design by addressing issues in the early stages of the design process.

When to Conduct Usability Testing
Usability testing can be conducted in various phases:
1.Before Design
Usability studies in the pre-design phase are suitable when you have an early concept of the product and a tangible prototype for users to test. For example, if you’re developing an app and have a clear idea of its purpose, usability testing can be initiated. However, ensure that a prototype is available for user testing to identify potential usability issues.
Another scenario for pre-design testing is when you plan to redesign an existing product by addressing current user pain points.
2.During Design
Usability testing can also occur during the design phase, playing a crucial role in the iterative design process. It enables the evaluation of the usability of design concepts, identification of potential issues, and informed design decision-making.
3.Post Launch
After the product launch, usability testing helps understand how users interact with the product in the real world. It provides insights into whether users encounter difficulties while using the product.
Core Elements of Usability Testing
There are many diverse types of usability testing, but the core elements in the most usability tests are;
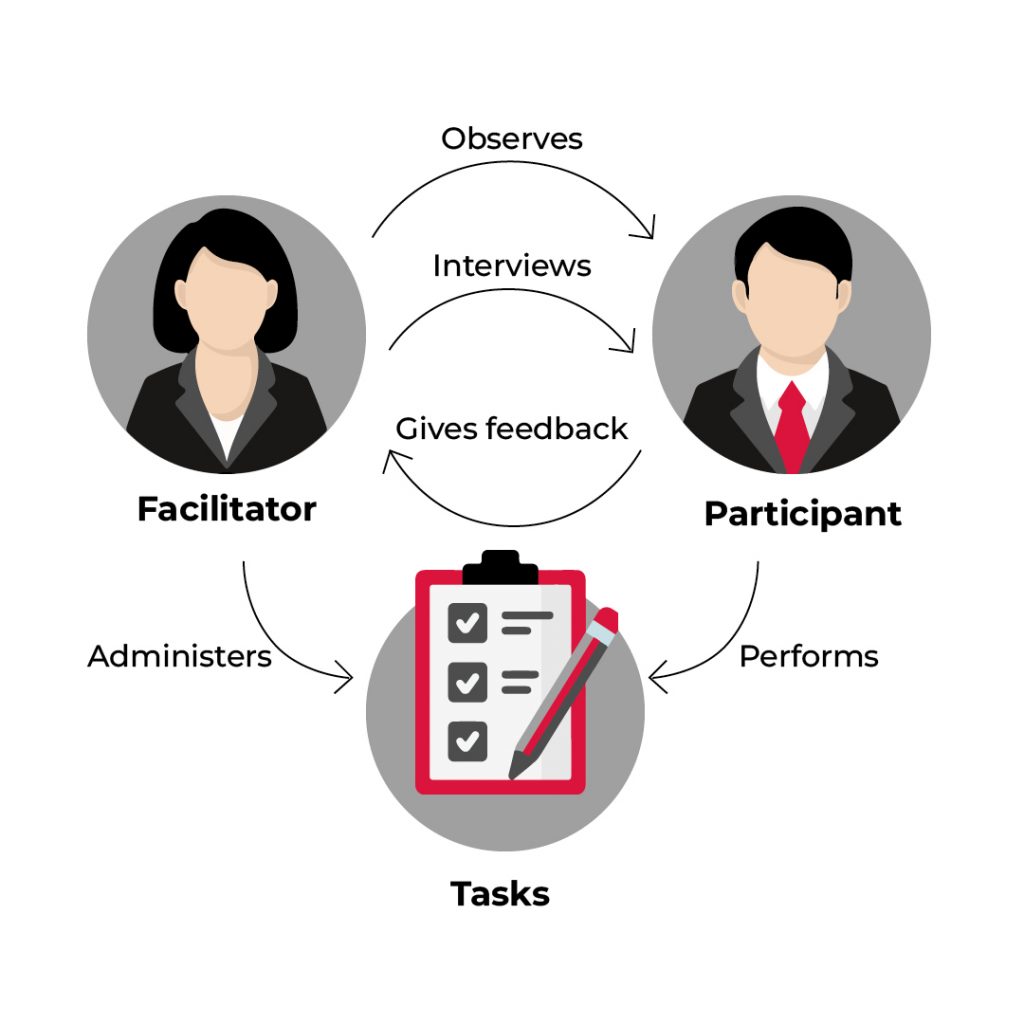
Usability testing comprises various elements, but the core components include:
1. Facilitator
The role of a facilitator in usability testing is pivotal for ensuring a smooth and productive testing session. The facilitator sets up the testing environment with the necessary equipment, software, and materials. They also welcome participants and establish rapport to create a positive testing environment that encourages honest feedback.
The facilitator explains the testing process to participants, emphasizing its purpose, and guides them through each task. During testing, the facilitator encourages participants to vocalize their thoughts and feelings as they interact with the design. Observations are made on participants’ behavior, comments, and any difficulties they encounter. The facilitator ensures the testing session stays on track and that participants complete required tasks within the allotted time. They can provide additional guidance if participants encounter difficulties. After the session, the facilitator thanks the participants and addresses any questions or concerns.
2. Participants
Participants should represent realistic users of the product or service under study. They may be current users of the product or have a similar background to the target user group. Participants are often encouraged to ‘think aloud’ during usability testing, narrating their actions and thoughts to understand their behaviors, goals, thoughts, and motivations.
3. Tasks
In usability testing, tasks are the primary components that participants perform to assess the product’s usability. These tasks simulate real-world scenarios and user interactions. The choice of tasks depends on the goals and objectives of the usability test.
Common usability testing tasks include onboarding processes (e.g., registration) and scenario-based tasks (e.g., booking a flight, or purchasing a product).
Usability Testing Environment
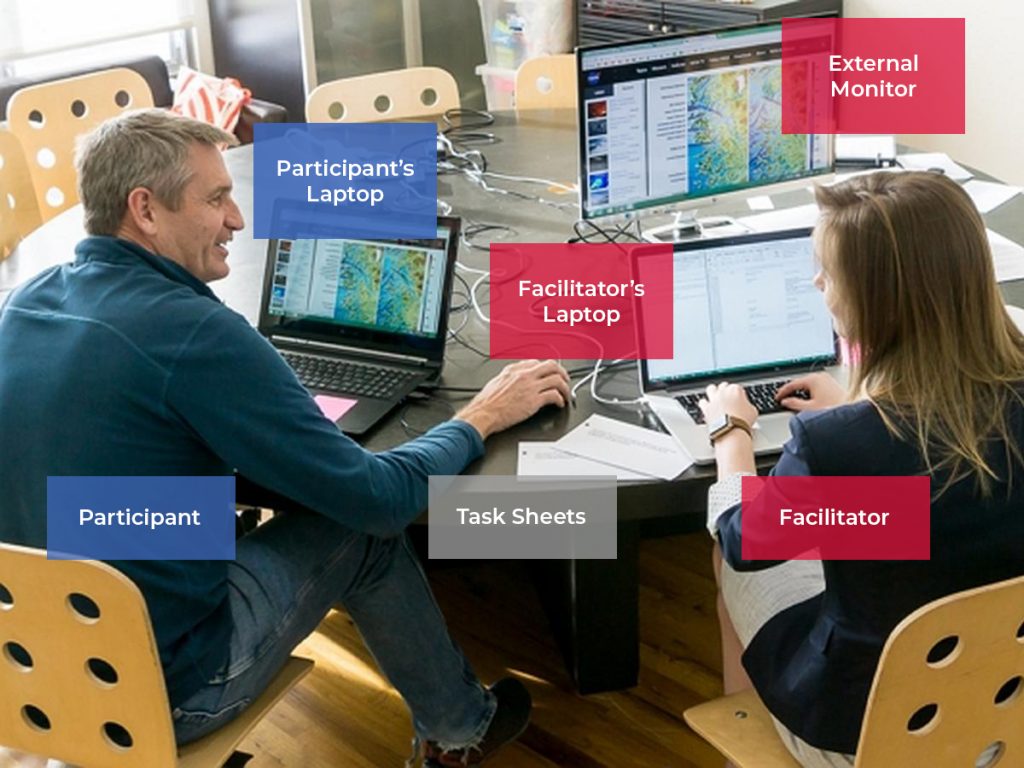
The above image demonstrates a typical in-person usability testing environment consisting of a participant seated on the left side and a facilitator on the right side. The facilitator explains tasks to the participant, who uses a laptop with screen recording software and a webcam to capture facial expressions and behaviors. The facilitator guides the participant through tasks, takes notes, and listens to participant feedback.
Remote Usability Testing
There are two types of remote usability testing:
1. Moderated
In moderated testing, participants and facilitators are in different physical locations. Facilitators interact with participants through screen-sharing software like Teams, Go-To-Meeting, or Skype. This approach allows facilitators to build rapport, guide participants, and ask questions in real time.
2. Unmoderated
Unmoderated testing lacks facilitator interaction. Instead, facilitators use remote testing tools to assign tasks to participants. Participants complete tasks at their convenience. After completing a task, the testing tools provide recordings and task data to researchers. Unmoderated testing offers the advantage of flexibility and participant comfort, allowing for honest feedback.
How To Conduct Remote Usability Testing
1. Setting up the environment
- Begin by building rapport with participants to ensure their comfort, which encourages honest feedback.
- Express gratitude to participants for their valuable time in participating in the usability study.
- Seek permission to video record the testing session.
- Explain the tasks participants will perform.
- Remind participants to provide honest feedback for design improvement, emphasizing that they are not being tested.
- Avoid forcing participants to complete tasks; the facilitator’s role is to gather information for a more user-friendly product.
2. Data capture
- Gather basic participant information, such as age and location.
- Record the device used for interacting with the design.
- Track the time taken to complete each task.
- Document participant comments while using the product.
- Observe participant actions and gestures.
- Note questions participants ask during task completion.
- Record suggestions and recommendations from participants.
Participants Data Capturing Form
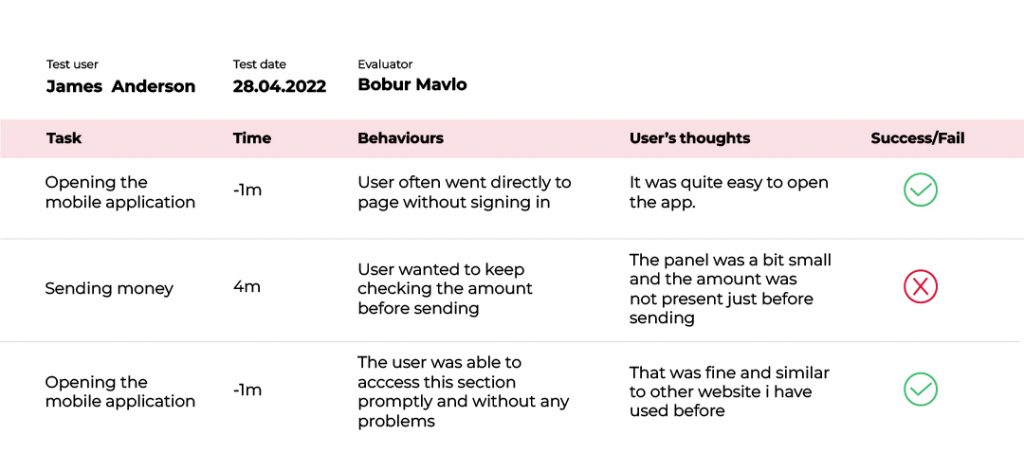
This is an example of a user testing form. Through this form the facilitators are capturing the user’s feedback against each task they are asked to perform.
The above image includes task details such as:
- Recording the time taken by the user to complete each task.
- Opening mobile applications, sending money, changing passwords, etc.
- Observing and documenting user behavior during each task.
- Collecting user feedback and thoughts on each task.
- Assessing whether each task was successfully completed or resulted in a failure.
Based on the findings from usability testing, the design team should iterate on the design and repeat the testing process to evaluate the effectiveness of the changes. This iterative process leads to a more user-friendly product.
In conclusion, usability testing serves as an indispensable tool for product evaluation. By involving real users in the process, it uncovers areas of struggle, frustration, and difficulty within the product’s design. This practice not only aids designers and developers in identifying and rectifying issues but also provides profound insights into user behavior and preferences. Early problem detection through usability testing reveals valuable opportunities for enhancing the design, ultimately creating a more user-centric and effective product.

